栈 Created 2020-05-11 | Updated 2022-05-22
| Post Views:
前言 栈是为了限制插入,删除只能在末端的一种表 。栈通常的操作有Push和Pop。
顺序栈 第一种
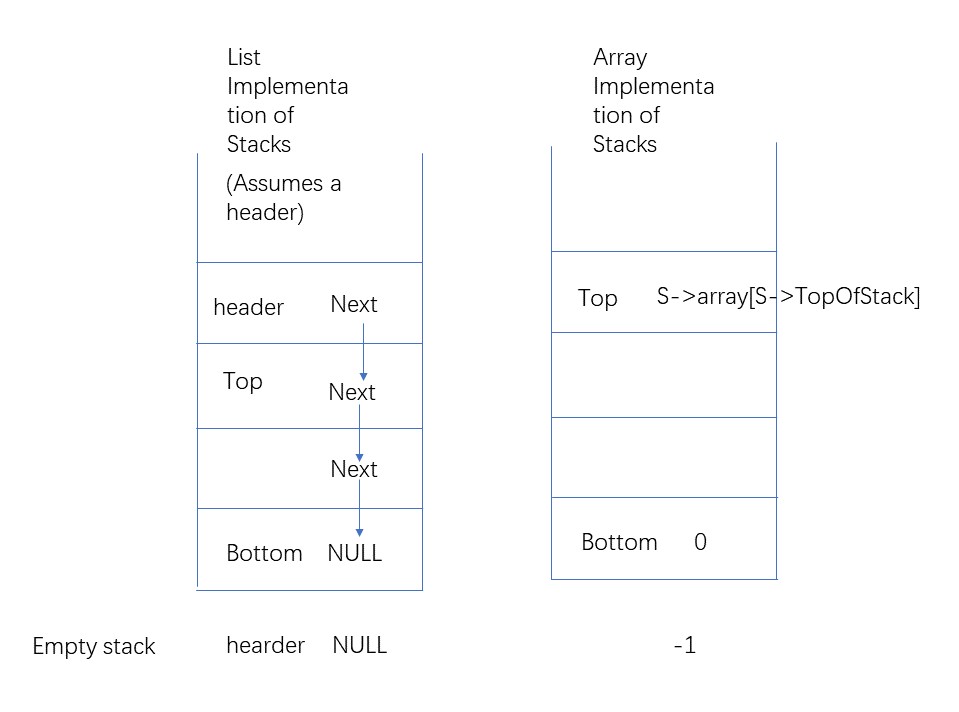
顺序栈用数组实现 。定义一个结构中有存放数据的数组(data[]),以及表明栈顶的数组下标(top) 。
进行Push和Pop操作的时候,通过给top++;来表面栈在数组中增添位置 。
空栈 顺序栈以数组来实现,所以下标为0时为第一个元素。当S->top = -1即一个元素也没有。
满栈 当数组下标top - 1时,数组被占满。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 #ifndef _STACK_H_ #define MAXSIZE 20 typedef int SElementType;typedef struct { SElementType data[MAXSIZE]; int top; } SqStack; void Push (SqStack *S, SElementType e) ;SElementType Pop (SqStack *S) ; #endif
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include "stack.h" void Push (SqStack *S, SElementType e) { if (S->top == MAXSIZE - 1 ) { fprintf (stderr , "Out of space." ); exit (1 ); } S->top++; S->data[S->top] = e; } SElementType Pop (SqStack *S) { if (S->top == -1 ) { fprintf (stderr , "The Stack is Empty" ); exit (1 ); } S->top--; return S->data[S->top]; }
第二种
TopOfStack记录数组顶栈的下标
Capacity记录数组的最大可容纳项数
动态allocate数组内存
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 #ifndef _Stack_h #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #define Error(str) fprintf(stderr, "%s\n" , str),exit(1) #define EmptyTOS (-1) typedef int ElementType;typedef struct StackRecord *Stack ;typedef struct StackRecord { int Capacity; int TopOfStack; ElementType *array ; }StackRecord; Stack CreateStack (int MaxElements) ; void MakeEmpty (Stack S) ;void DisposeStack (Stack S) ;int IsEmpty (Stack S) ;int IsFull (Stack S) ;void Push (ElementType e, Stack S) ;ElementType Top (Stack S) ; void Pop (Stack S) ;ElementType TopAndPop (Stack S) ; void Traverse (Stack S) ;#endif
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 #include "stack.h" Stack CreateStack (int MaxElements) { Stack S = malloc (sizeof (StackRecord)); S->array = malloc (sizeof (ElementType) * MaxElements); if (!S) Error("Out of space." ); S->Capacity = MaxElements; MakeEmpty(S); return S; } void MakeEmpty (Stack S) { S->TopOfStack = EmptyTOS; } void DisposeStack (Stack S) { if (S != NULL ) { free (S->array ); free (S); } } int IsEmpty (Stack S) { return S->TopOfStack == EmptyTOS; } int IsFull (Stack S) { return S->TopOfStack == S->Capacity - 1 ; } void Push (ElementType e, Stack S) { if (IsFull(S)) Error("Full stack" ); else S->array [++S->TopOfStack] = e; } ElementType Top (Stack S) { if (!IsEmpty(S)) return S->array [S->TopOfStack]; Error("Empty stack" ); } void Pop (Stack S) { if (!IsEmpty(S)) S->TopOfStack--; else Error("Empty stack" ); } ElementType TopAndPop (Stack S) { if (!IsEmpty(S)) { return S->array [S->TopOfStack--]; } Error("Empty stack" ); } void Traverse (Stack S) { for (int i = S->TopOfStack; i > EmptyTOS ; i--) printf ("%d " , S->array [i]); printf ("\n" ); }
链栈 有头节点的栈
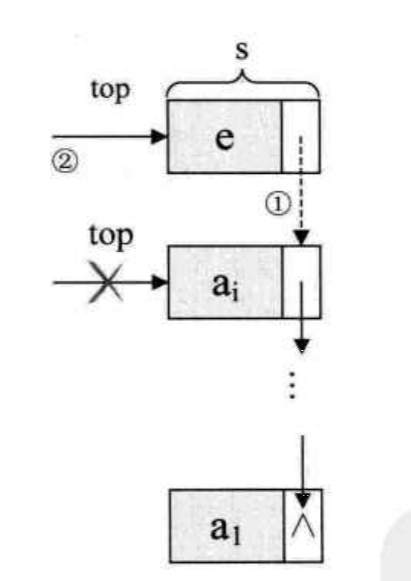
空栈 首先创建一个头节点。让头节点的next = NULL。随后的Push操作在前端进行 它和单链表的结构声明一样。就是属性和操作不一样 。
示例 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 #ifndef _Stack_h_ #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #define Error(str) fprintf(stderr, "%s\n" , str),exit(1) typedef int ElementType;typedef struct Node *PtrToNode ;typedef PtrToNode Stack;typedef struct Node { ElementType e; PtrToNode Next; }Node; int IsEmpty (Stack S) ;Stack CreateStack (void ) ; void MakeEmpty (Stack S) ;void Pop (Stack S) ;void Push (ElementType X, Stack S) ;ElementType Top (Stack S) ; void Traverse (Stack S) ;#endif
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 #include "stack.h" int IsEmpty (Stack S) { return S->Next == NULL ; } Stack CreateStack (void ) { Stack S; S = (Stack)malloc (sizeof (Node)); if (S == NULL ) Error("Out of space." ); S->Next = NULL ; MakeEmpty(S); return S; } void MakeEmpty (Stack S) { if (S == NULL ) Error("Must create a stack." ); else while (!IsEmpty(S)) Pop(S); } void Pop (Stack S) { Stack FirstCell; if (IsEmpty(S)) Error("Empty stack" ); else { FirstCell = S->Next; S->Next = S->Next->Next; free (FirstCell); } } void Push (ElementType e, Stack S) { PtrToNode TmpCell; TmpCell = malloc (sizeof (Node)); if (TmpCell == NULL ) Error("Out of space!!!" ); else { TmpCell->e = e; TmpCell->Next = S->Next; S->Next = TmpCell; } } ElementType Top (Stack S) { if (IsEmpty(S)) Error("Empty stack." ); return S->Next->e; } void Traverse (Stack S) { PtrToNode Cell = S->Next; while (Cell != NULL ) { printf ("%d " , Cell->e); Cell = Cell->Next; } printf ("\n" ); }
无头节点的栈
StackNode 它表面顶栈(top)。当中包含顶栈的数据(data)和指向前一项的指针(next)
LinkStack 它表面整个栈(可实际上只有栈顶可见)。当中包含指向栈顶(top)的指针,和目前所分配的项(Node)的数量。
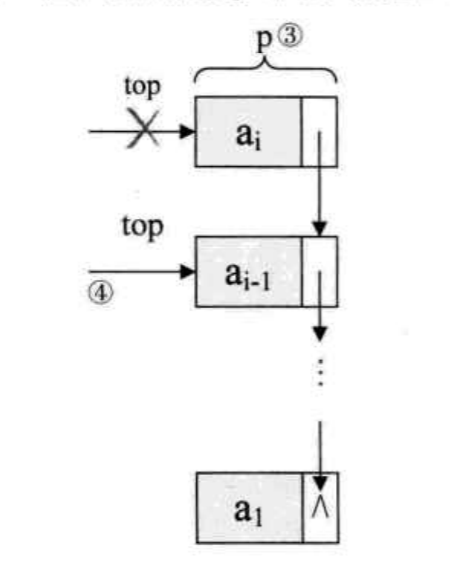
链栈的next的指向与链表不同 ,当我们使链栈为空的时候,需要malloc一个链栈(LinkStack),让S->top = NULL;cout = 0
示例 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 #ifndef _LinkStack_H_ typedef int SElementType;typedef struct StackNode { SElementType data; struct StackNode *next ; } StackNode, *LinkStackPtr; typedef struct LinkStack { LinkStackPtr top; int count; }LinkStack; void Push (LinkStack *S, SElementType e) ;void Pop (LinkStack *S, SElementType *e) ;#endif
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include "liststack.h" void Push (LinkStack *S, SElementType e) { LinkStackPtr s = (LinkStackPtr)malloc (sizeof (StackNode)); s->data = e; s->next = S->top; S->top = s; S->count++; } void Pop (LinkStack *S, SElementType *e) { LinkStackPtr p; if (S->count == 0 ) { fprintf (stderr , "The stack is empty" ); exit (1 ); } *e = S->top->data; p = S->top; S->top = S->top->next; free (p); S->count--; }