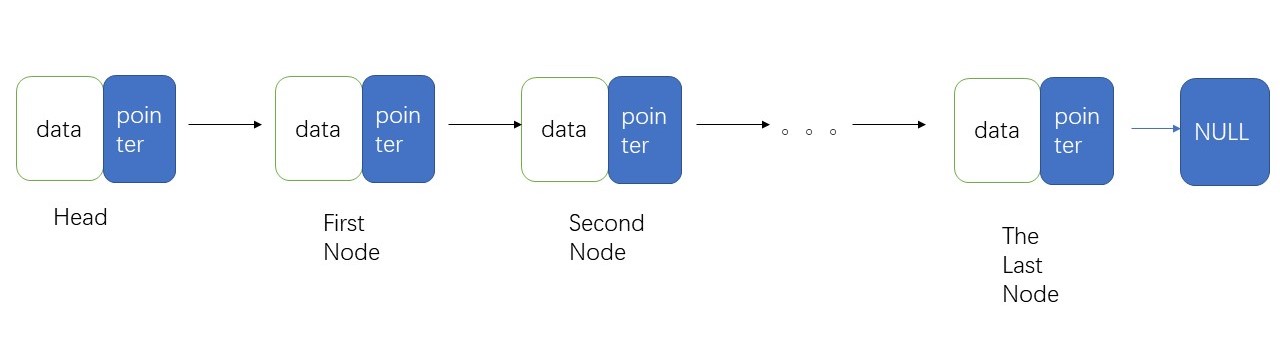
线性表的链式存储结构 Created 2020-05-09 | Updated 2022-05-22
| Post Views:
前言 拥有头节点的链表
头节点的date区可以存放链表的整体数据(例如:长度)
实现接口 遍历链表 遍历链表一般使用while循环。相关操作有:GetElement() ListLength() Insert()很多很多都可以使用遍历链表来实现
虽然当我们的函数参数为(结构指针)的时候,在函数中改变指针的指向,不会影响到指针的指向。但是,如果我们传递结构指针的指针来改变指针的指向呢?(例如:malloc创建节点)
1 2 3 4 5 while (P != NULL && count < i){ P = P->next; count++; }
一真全真 1 2 3 4 5 if (P == NULL || count < i){ fprintf (stderr , "List has not No.%d element" , i); exit (1 ); }
插入节点 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 void Insert (List L, int i, ElementType e) { Position P, N; int count = 1 ; P = L; while (P != NULL && count < i) { P = P->next; count++; } if (P == NULL || count < i) { fprintf (stderr , "List has not No.%d element" , i); exit (1 ); } N = (Position)malloc (sizeof (Node)); N->e = e; N->next = P->next; P->next = N; }
注意 N->next = P->next;和P->next = N这两句顺序不能反 。(即,从another节点的next指向N节点的后一个节点,再让N的后一个节点指向another节点。)否则,一开始就把before的后一节点覆盖,那么就这个链就断裂了 。所以,要先要对another节点操作 。
删除节点 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 void DeList (List L) { Position P, Q; P = L->next; while (Q != NULL ) { Q = P->next; free (P); P = Q; } L->next = NULL ; }
注意 这里需要先定义两个位置Position P, Q。因为要循环删除节点,后一个节点的地址不能丢,所以要创建两个结构指针。首先Q = P->next记录P的next ,free(P),释放P。这时P里不再有next指针 ,再让P = Q(让P指向下个节点) 。
示例 list.h 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 #ifndef _List_H #define _List_H #include <stdio.h> typedef int ElementType;typedef struct Node *PtrToNode ;typedef PtrToNode Position;struct Node { ElementType e; PtrToNode next; } Node; typedef PtrToNode List;void InitList (List *L) ;ElementType GetElement (List L, int i) ; void Insert (List L, int i, ElementType e) ;int ListLength (List L) ;void Traverse (List L) ;void DeList (List L) ;#endif
list.c 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 #include "list.h" #include <time.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> void InitList (List *L) { *L = (PtrToNode)malloc (sizeof (Node)); if (*L == NULL ) { fprintf (stderr , "out of space." ); exit (1 ); } (*L)->next = NULL ; } typedef List LinkList;void CreateListTail (LinkList *L, int n) { LinkList p,r; int i; srand(time(0 )); *L = (LinkList)malloc (sizeof (Node)); r=*L; for (i=0 ; i<n; i++) { p = (PtrToNode)malloc (sizeof (Node)); p->e = rand()%100 +1 ; r->next=p; r = p; } r->next = NULL ; } ElementType GetElement (List L, int i) { Position P; int count = 1 ; P = L->next; while (P != NULL && count != i) { P = P->next; count++; } if (P == NULL || count < i) { fprintf (stderr , "List has not No.%d element" , i); exit (1 ); } return P->e; } void Insert (List L, int i, ElementType e) { Position P, N; int count = 1 ; P = L; while (P != NULL && count < i) { P = P->next; count++; } if (P == NULL || count < i) { fprintf (stderr , "List has not No.%d element" , i); exit (1 ); } N = (Position)malloc (sizeof (Node)); N->e = e; N->next = P->next; P->next = N; } int ListLength (List L) { int count = 0 ; L = L->next; while (L != NULL ) { L = L->next; count++; } return count; } void Traverse (List L) { Position P = L->next; while (P != NULL ) { printf ("%d " , P->e); P = P->next; } printf ("\n" ); } void DeList (List L) { Position P, Q; P = L->next; while (Q != NULL ) { Q = P->next; free (P); P = Q; } L->next = NULL ; }
test.c 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include "list.h" int main () { List L; InitList(&L); printf ("After Initialize the length of list is %d\n" , ListLength(L)); for (int i = 0 ; i < 5 ; i++) { Insert(L, i + 1 , i); } printf ("After Insert the length of list is %d\n" , ListLength(L)); Traverse(L); DeList(L); printf ("After Delete the list the length of list is %d\n" , ListLength(L)); }