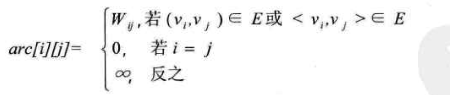图的存储结构 Created 2020-05-26 | Updated 2022-05-22
| Post Views:
前言 由于图的多方向性,不能用顺序存储结构来实现。如果我用多重链表的话,那么结构中的多个指针就会造成空间资源的浪费(因为图的顶点上的度是不确定的)。因此图的存储结构,不应该使用物理存储去实现。图的实现被提供了5种存储结构。1. 邻接矩阵 2.邻链表 3.十字链表 4. 邻接多重链表 5. 边集数组。
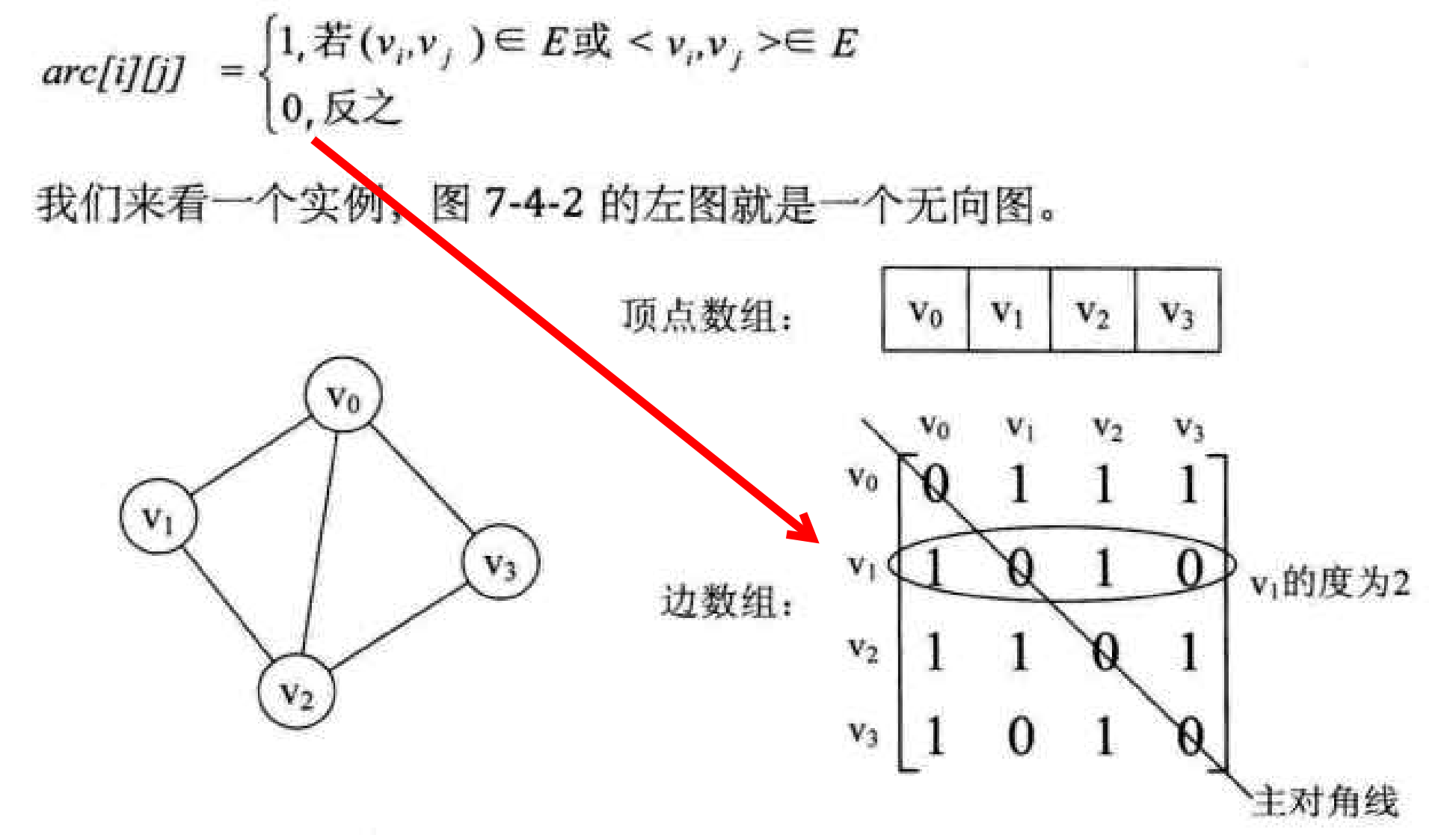
邻接矩阵 由顶点数组(一维)和边或弧数组(二维)组成
无向图
例如a[i][j]的0,1值表示,从i–j这个edge是否存在,1存在,0不存在 。a[i][i]这样的顶点到顶点的值都为0
无向图的边数组是一个对称矩阵 ,即满足a[i][j] == a[j][i]在无向图中a[i][j]和a[j][i]无区别
Vi的度 就是把第i行(或列)的元素加起来
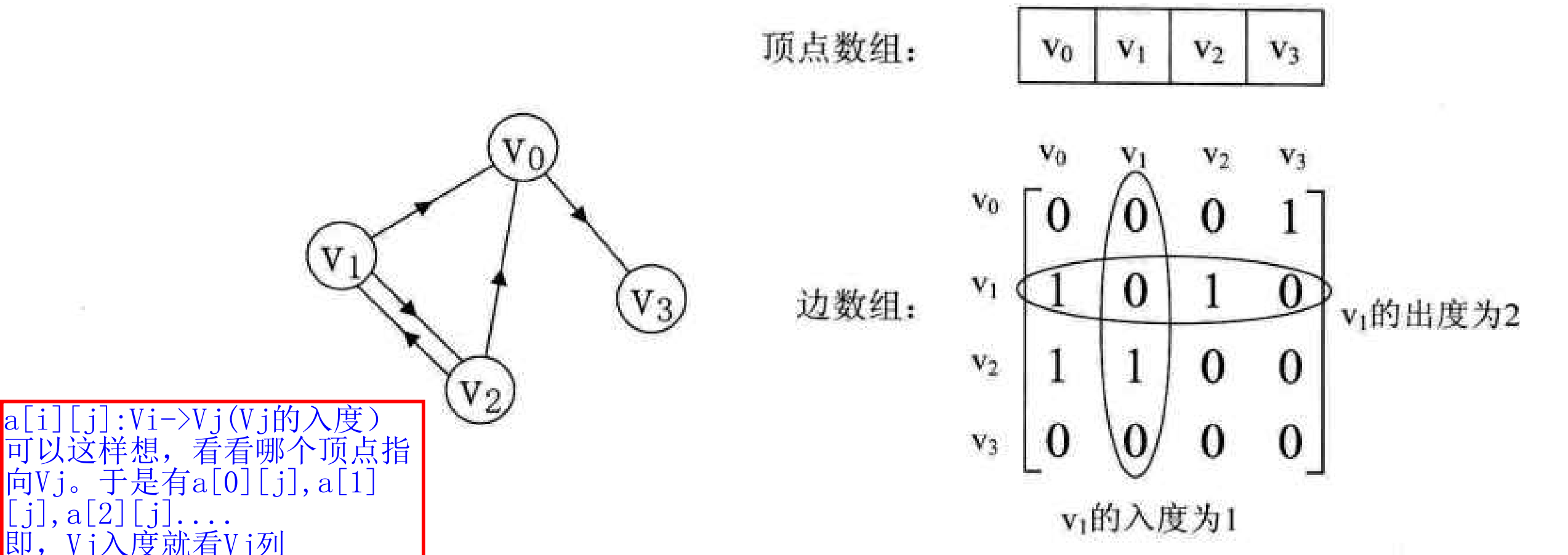
有向图
有向图就不是对称矩阵了 。因为它们顶点的指向是有方向的,i–>j不一定j–>i。
出度和入度。有向图中,要研究这两个。只要知道前面的指向问题,就可以知道。Vi的出度是看矩阵中的行a[i]--[],Vi的入度是看矩阵中的列a[]--[i]。将行或列加起来就是出度和入度的值了 。
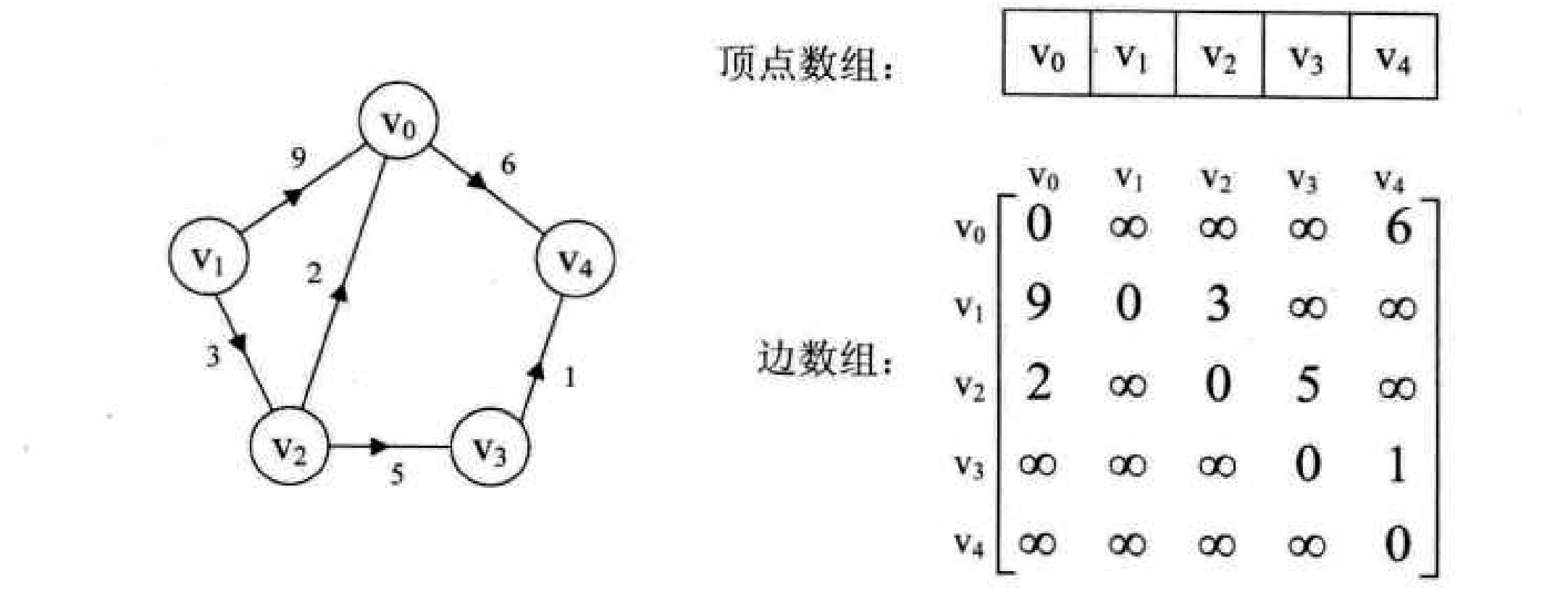
网Network 网就是每条edge上带有权的图
矩阵上的值
无向图的创建 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 #ifndef _Graph_H #include <stdbool.h> #include <stdio.h> typedef char VertexType;typedef int EdgeType;#define MAXVEX 100 #define INFINITY 65535 bool visited[MAXVEX];typedef struct { VertexType vexs[MAXVEX]; EdgeType arc[MAXVEX][MAXVEX]; int numVertexs, numEldge; }MGraph; void CreateMGraph (MGraph *G) ;void DFS (MGraph G, int i) ;void DFSTraverse (MGraph G) ;#endif
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 #include "graph.h" void CreateMGraph (MGraph *G) { int i, j, k, w; printf ("Enter the number of Vertexs and edge:" ); scanf ("%d %d" , &G->numVertexs, &G->numEldge); printf ("Enter the information of Vertexs array:" ); for (i = 0 ; i < G->numVertexs; i++) scanf (" %c" , &G->vexs[i]); for (i = 0 ; i < G->numEldge; i++) for (j = 0 ; j < G->numEldge; j++) G->arc[i][j] = MAXVEX; for (k = 0 ; k < G->numEldge; k++) { printf ("Enter double dimensional array indexs and weight of the edges:" ); scanf ("%d %d %d" , &i, &j, &w); G->arc[i][j] = w; G->arc[j][i] = G->arc[i][j]; } }
邻接表 邻接矩阵如果要处理顶点很多,而边很少 的图那么会造成空间的浪费。所以,引入邻接表来避免这种现象发生。
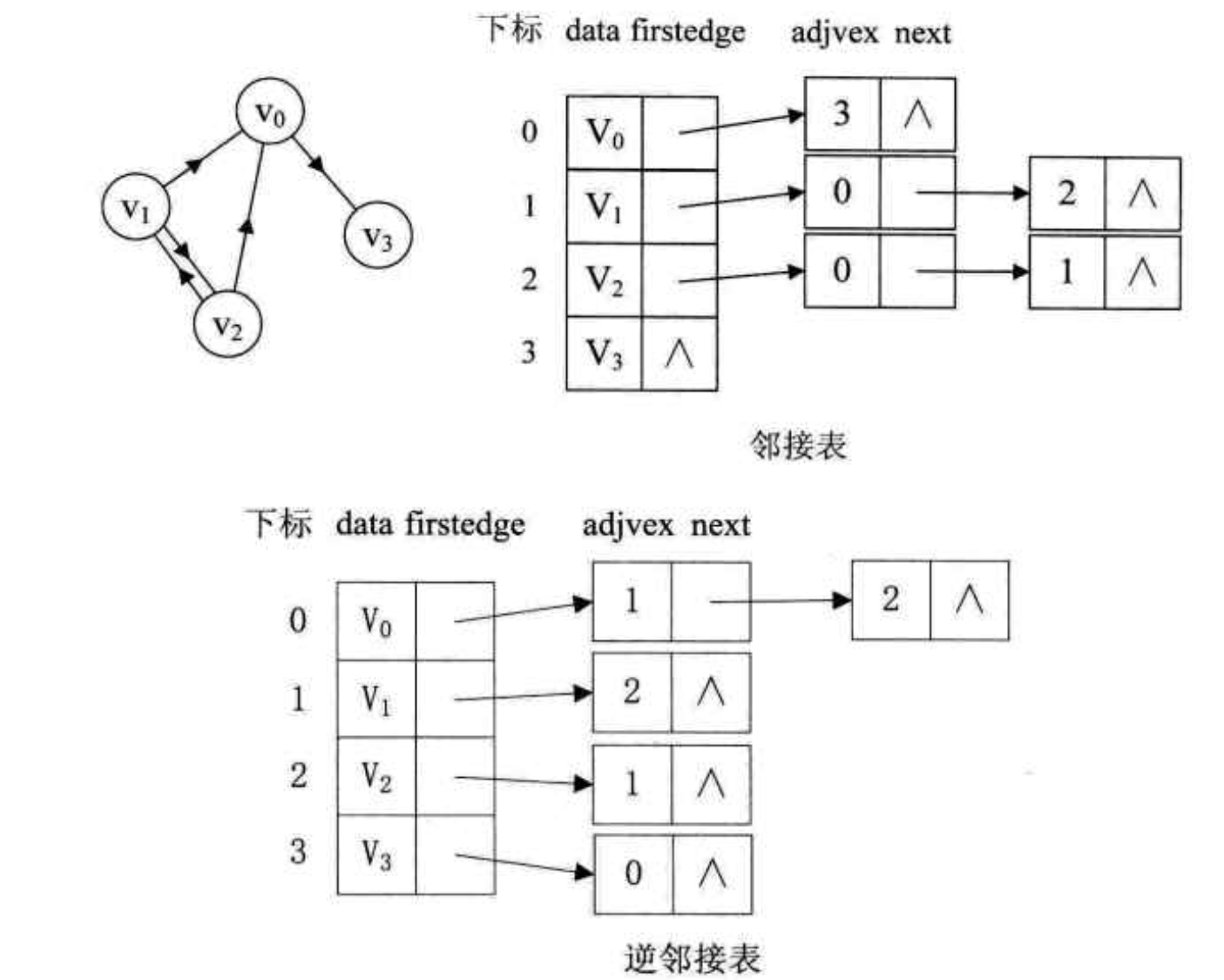
结构数组。每个数组的元素是代表每个顶点 。每个结构包含链表节点指针(firstedge),每个顶点类型(data(V1 ,V2))
1 2 3 4 5 typedef struct VertexNode //顶点表节点{ VertexType data; EdgeNode *firstedge; }VertexNode, AdjList[MAXVEX];
链表。每个节点包含顶点下标值(i(Vi)),权值,指向下一个节点点指针(next)
1 2 3 4 5 6 typedef struct EdgeNode //边表节点{ int adjvex; EdgeType weight; struct EdgeNode *next ; }EdgeNode;
然鹅,如果是面对有向图的话,因为弧有方向,所以有出度和入度。这样一来,这个邻接表,又可以分为两种。以弧头为链表的头(邻接表方便计算出度),以弧尾为链表的表头(逆邻接表方便计算入度) 。
创建 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 #ifndef _List_H #define MAXVEX 100 typedef char VertexType;typedef int EdgeType;typedef struct EdgeNode //边表节点{ int adjvex; EdgeType weight; struct EdgeNode *next ; }EdgeNode; typedef struct VertexNode //顶点表节点{ VertexType data; EdgeNode *firstedge; }VertexNode, AdjList[MAXVEX]; typedef struct //整个邻接表{ AdjList adjList; int numVertexs, numEdges; }GraphAdjList; void CreateAdjList (GraphAdjList *G) ;#endif
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include "list.h" void CreateAdjList (GraphAdjList *G) { int i, j, k; EdgeNode *e; printf ("Enter the number of Vertexs and edges:" ); scanf ("%d %d" , &G->numVertexs, &G->numEdges); printf ("Enter the elements of Vertexs List:" ); for (i = 0 ; i < G->numVertexs; i++) { scanf ("%c" , &G->adjList[i].data); G->adjList[i].firstedge = NULL ; } for (k = 0 ; k < G->numEdges; k++) { printf ("Enter the value of i and j with the edge(Vi,Vj):" ); scanf ("%d %d" , &i, &j); e = malloc (sizeof (EdgeNode)); e->adjvex = j; e->next = G->adjList[i].firstedge; G->adjList[i].firstedge = e; e = malloc (sizeof (EdgeNode)); e->adjvex = i; e->next = G->adjList[i].firstedge; G->adjList[j].firstedge = e; } }
十字链表 因为邻接表容易解决出度情况,要想了解入度就要遍历整个表才能知道。而逆邻接表也有这个情况。如果我们想要将两者的优势互补,就引入了十字链表。