双链表交换元素
Created|Updated
|Post Views:
前言
双链表和单链表的插入,删除,交换。可以想象成锁链,但是,前后的链不能断开联系
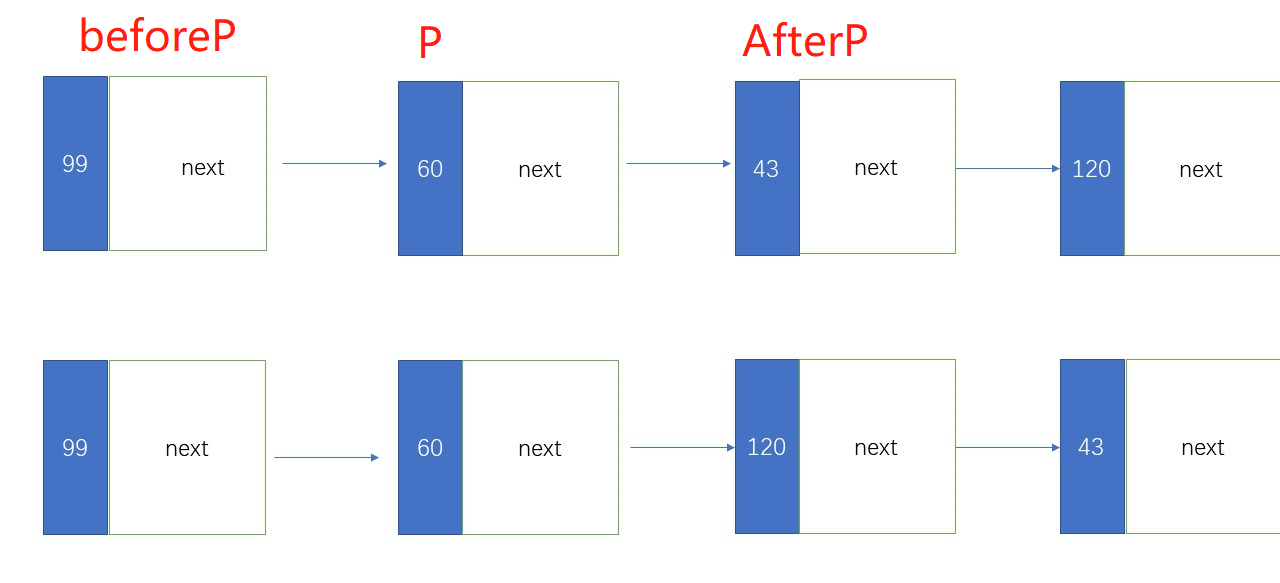
交换
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| void SwapWithNextAndLast(Position BeforeP)
{
Position P = BeforeP->next;
Position AfterP = P->next;
P->next = AfterP->next;
BeforeP->next = AfterP;
AfterP->next = P;
P->next->last = P;
P->last = AfterP;
AfterP->last = BeforeP;
}
|
插入
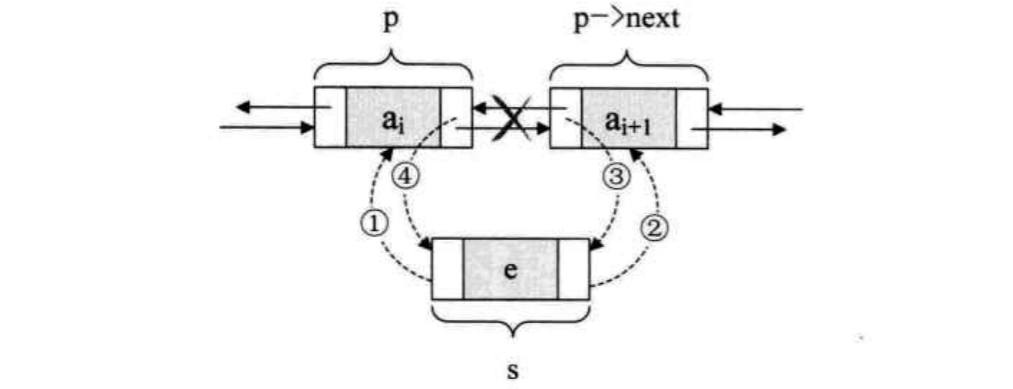
*只要把S指针与前后相连,S->next,S->prior与前后指针相连。*就完成了。
- 把S的prior,next搞定
- 再将After的prior与S连上,为了不断线
- 最后,切断Before的next与After的联系,与S连上
1
2
3
4
5
| S->prior = P;
S->next = P->next;
P->next->prior = S;
P->next = S;
|
示例
双链表的实现和交换元素1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
| #include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
typedef struct Node * PtrToNode;
typedef PtrToNode List;
typedef PtrToNode Position;
void SwapWithNextAndLast(Position BeforeP);
void PrintTail(List T);
struct Node
{
int e;
Position last;
Position next;
};
int main()
{
List L = NULL, T;
Position prev = NULL, current;
int n = 0;
while (n < 4)
{
current = (PtrToNode)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
if(L == NULL)
L = current;
else
prev->next = current;
current->last = prev;
current->next = NULL;
current->e = n++;
prev = current;
}
T = prev;
PrintTail(T);
SwapWithNextAndLast(L);
PrintTail(T);
return 0;
}
void SwapWithNextAndLast(Position BeforeP)
{
Position P = BeforeP->next;
Position AfterP = P->next;
P->next = AfterP->next;
BeforeP->next = AfterP;
AfterP->next = P;
P->next->last = P;
P->last = AfterP;
AfterP->last = BeforeP;
}
void PrintTail(List T)
{
while (T != NULL)
{
printf("%d ", T->e);
T = T->last;
}
printf("\n");
}
|



